How Standards Drive and Evolve with Innovation
To many people, standards are a roadblock to innovation when, in actuality, standards help accelerate Innovation
Aaron’s Thoughts On The Week
“No matter how good you get you can always get better, and that's the exciting part.” -Tiger Woods
Since joining ASTM International, I have seen the launch of numerous new standards efforts within ASTM and at many of my fellow Standards Development Organizations (SDOs). For those who know me, I do not hesitate to point to standards work regardless of who worked on them and published them.
For those of us who are gifted at developing standards and making a career out of it, we cheer each other on because we know this is a thankless role to the vast majority of the public. We don’t always produce precisely what everyone wants. We sometimes have to be taskmasters to the volunteers working on the standards. We sometimes have to play referee between two or more groups. We can put a smile on a person’s face or cause them to cry. Still, we know we are part of the more prominent family of keepers of “doing the right thing.” Because that is what having standards are, making the best effort to do the right thing for most people and their products.
This is why it is a bit disheartening when people say that standards stifle innovation. I counter, “How can you identify what to innovate without a benchmark to measure your ‘innovation’ against?”
It is one thing to say your product or breakthrough is an improvement. It is pretty different, though, when you have a standard that has already set a benchmark, and by using the standard, you can show how much your innovation improves on it.
If you can't measure your innovation, can you call it innovative?
Innovation is often heralded as the lifeblood of progress, driving technological advancements, business, and society. However, the true impact of an innovation can only be assessed if it is measurable. Without concrete metrics, it becomes challenging to differentiate genuine innovation from mere novelty. Here’s why measurement is crucial to validating innovation:
Objective Evaluation
Metrics provide a standardized way to evaluate the effectiveness and impact of an innovation. They allow stakeholders to objectively assess whether the innovation meets its intended goals and delivers tangible benefits. For instance, a new software feature might be innovative if it significantly improves user efficiency. However, this can only be confirmed through measurable outcomes like reduced task completion times or increased user satisfaction scores.
Benchmarking and Comparison
Measurement enables benchmarking against existing solutions or industry standards. One can determine if an innovation truly offers improvements or advancements by comparing it to what currently exists. This comparison helps to highlight the innovation’s unique value proposition and justify its adoption. For example, a new manufacturing process might be considered innovative if it reduces production costs or increases output quality compared to traditional methods.
“How can you identify what to innovate without a benchmark to measure your ‘innovation’ against?”
Continuous Improvement
Innovation is not a one-time event but an ongoing process. Measuring its impact provides critical feedback that can drive continuous improvement. Metrics can reveal areas where the innovation falls short, allowing for iterative enhancements. This cycle of evaluation and refinement ensures that the innovation remains relevant and effective over time.
Resource Allocation
Organizations have limited resources and must prioritize investments that offer the highest returns. Measurable innovations allow companies to make informed decisions about where to allocate their resources. Clear metrics demonstrate the potential ROI of innovation, guiding strategic investments and minimizing risks associated with unproven ideas.
Validation and Credibility
Innovations that can be measured gain greater credibility and acceptance. Quantifiable evidence of success builds trust among stakeholders, including investors, customers, and partners. It shows that innovation isn’t just another theoretical concept but a proven solution that delivers real-world benefits. This credibility is essential for gaining support and scaling the innovation.
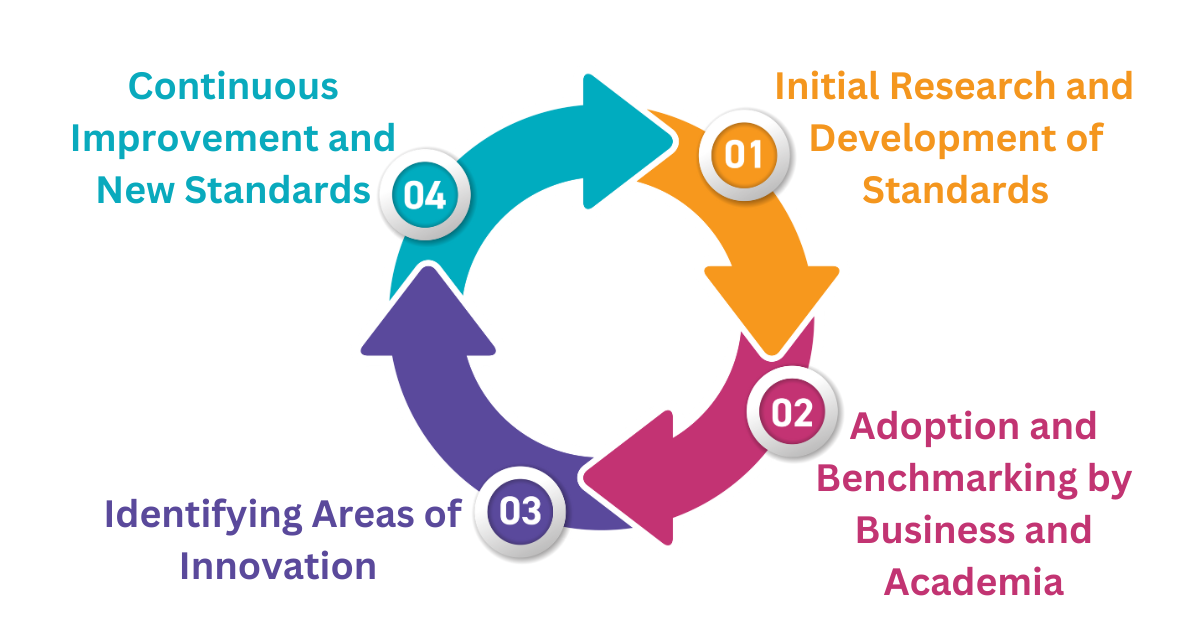
How The Standard Lifecycle Supports Innovation
Standards play a crucial role in fostering innovation by providing a solid foundation upon which research, business, and academia can build by setting a basis for benchmarking to evaluate everything from simple changes to genuine innovations. The development, application, and continuous improvement of standards create a virtuous innovation cycle. Here's how it works:
Initial Research and Development of Standards
The process starts with thorough research to establish the initial standard. Experts from different fields conduct studies, experiments, and analyses to create a set of guidelines and specifications that define the best practices and technical requirements for a specific product or process.
Standards, in turn, provide researchers with a roadmap, guiding their efforts and ensuring that their work aligns with industry needs and expectations. This alignment helps to avoid duplicate efforts and focuses resources on real advancements. With a benchmark in place, researchers can compare innovations against the established standards. This comparison helps to identify areas where existing technologies fall short and where improvements are needed, driving targeted innovation.
Adoption and Benchmarking by Business and Academia
After they are established, businesses and academic institutions adopt these standards. Companies use the standards to ensure that their products meet specific criteria, while researchers and educators use them as benchmarks to evaluate and compare different products and technologies.
This phase allows for consistent "apples-to-apples" comparisons, ensuring all products are assessed using the same criteria. Adhering to standards ensures product consistency and quality for businesses, which are critical for gaining customer trust and market acceptance. Standards also help companies meet regulatory requirements and reduce the risk of product failures or recalls. By exceeding baseline requirements, businesses can differentiate their products and market innovations as superior, offering a competitive edge.
Identifying Areas for Innovation
The benchmarking process often uncovers gaps, limitations, and areas for improvement within current standards. By comparing products side-by-side, businesses and researchers can pinpoint specific areas where innovation is necessary. This insight helps focus resources and efforts on developing new technologies and solutions to address these gaps.
Using insights from benchmarking, businesses and researchers innovate to create new products and processes that exceed existing standards. These innovations may involve new materials, advanced technologies, or improved methodologies to enhance performance, efficiency, and safety.
Continuous Improvement and New Standards
Innovations undergo rigorous testing and validation as they emerge. Successful innovations often lead to the revision and improvement of existing standards. The standards are updated to incorporate the latest advancements, ensuring they remain relevant and effective. Applying standards creates a feedback loop where real-world usage and performance data are collected and analyzed. This feedback informs the revision and improvement of existing standards to ensure they remain relevant and effective. Continuous benchmarking against standards helps identify new areas for innovation. Gaps and limitations revealed through this process drive the development of new technologies and methods, pushing the boundaries of what is possible.
In robotics, for example, the ASTM International's F45 Committee on Robotics, Automation, and Autonomous Systems develops standards that guide the design, manufacturing, testing, and implementation of robotic systems. These standards help businesses and researchers benchmark various robotic solutions, identify areas for improvement, and drive innovations that enhance robotic capabilities. As new technologies are developed, the standards are updated, creating a continuous innovation loop.
Every seven years, F45 must review and update its standards if needed. Failure to do such an update will result in the standards being removed from publication. This requirement forces F45 to ensure its standards reflect the marketplace’s needs and develop standards that move the industry forward. It also shows how Standards are not these locked-in-place pieces; they can and do end if no one is taking care of them.
This video of a tested mobile robot is based on two ASTM standards. One standard establishes how to set up the course and what items to place (or not to place) in it. The second standard involves testing the robot and recording all of the results. These results can then be duplicated by another lab anywhere in the world because they can use the same two standards. Also, the test gives the researchers a benchmaker to work against be it the same robot with new features added or against another robot running the same test.
The Virtuous Cycle of Standards and Innovation
The continuous cycle of research, benchmarking, innovation, and standard improvement is pivotal for industries aiming to stay at the forefront of technology. This iterative process begins with thorough research, identifying current trends, challenges, and opportunities within the industry. Benchmarking follows, allowing organizations to measure their performance against the best practices and standards established by leading entities. This comparison highlights areas for improvement and inspires new ideas and solutions.
Innovation is then driven by the insights gained from research and benchmarking. Industries leverage this information to develop cutting-edge technologies and processes that push the possible boundaries. However, innovation alone is not enough; it needs to be channeled through a structured framework to ensure it is effective and sustainable. This is where standards play a crucial role.
Standards provide a clear and consistent framework that guides the development and implementation of new technologies and processes. They set quality benchmarks that must be met, ensuring that innovations are reliable, safe, and efficient. By adhering to established standards, industries can ensure that their products and services meet or exceed customer expectations.
Moreover, standards drive progress by creating a common language and expectations within the industry. They facilitate collaboration between different entities, enabling sharing of knowledge and best practices. This collaborative environment fosters continuous improvement as companies learn from each other and collectively push the industry forward.
In essence, standards help industries achieve new heights of excellence and efficiency by providing a structured approach to innovation. They ensure that creativity is channeled productively, leading to high-quality outcomes that benefit both the industry and its consumers. Through this continuous cycle of research, benchmarking, innovation, and standard improvement, industries can maintain their competitive edge and drive sustained progress.
Robot News Of The Week
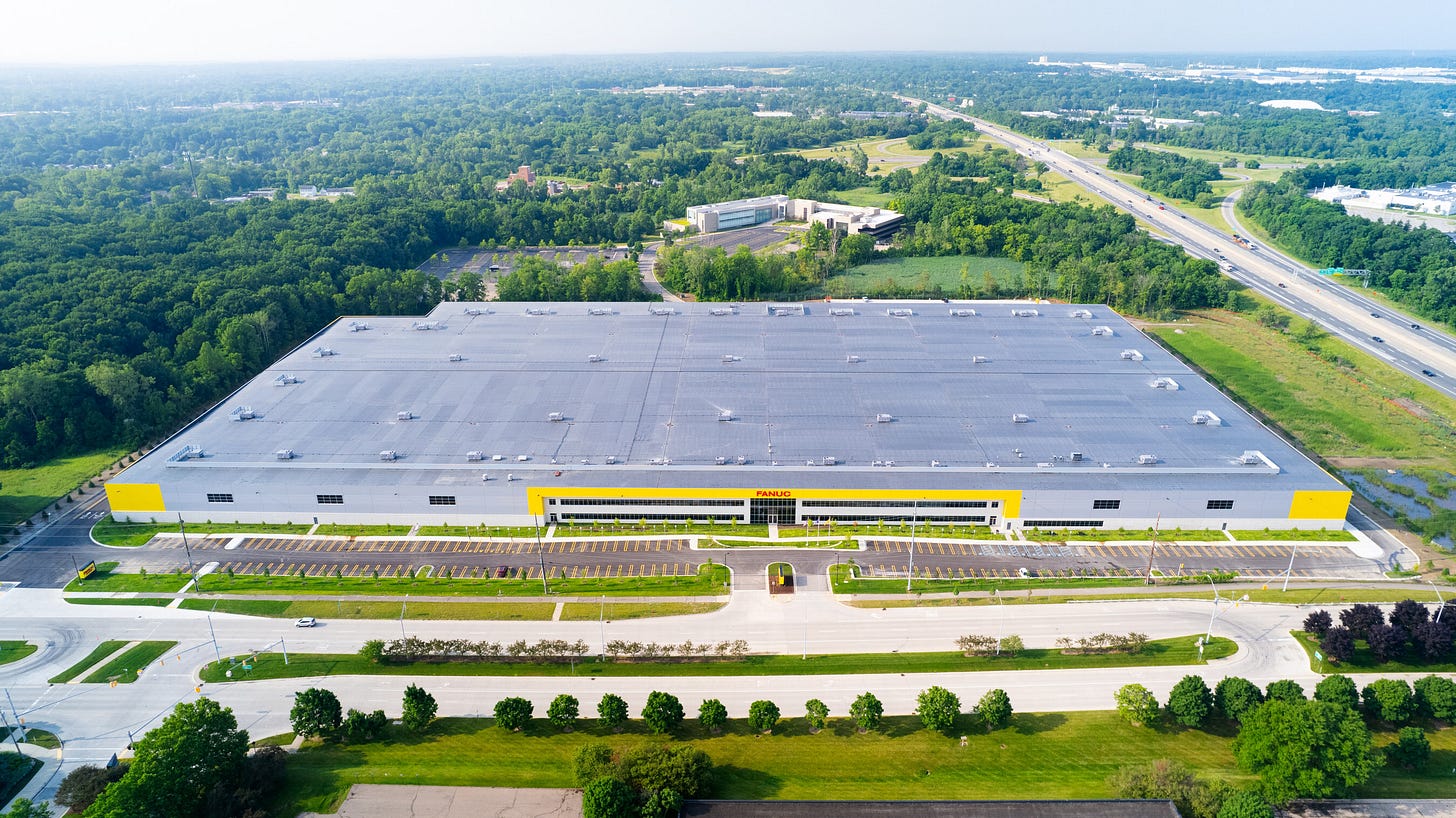
FANUC America Unveils New $110 Million Robotics and Automation Campus
FANUC America has unveiled its new 650,000-square-foot West Campus facility in Auburn Hills, Michigan, representing a $110 million investment built on 67 acres. The expansion is part of FANUC America's strategic investment plan to advance industrial automation in North America. The West Campus provides advanced product manufacturing and customized automation systems and includes warehouse space for over 6,000 quick-delivery robots and tens of thousands of parts. FANUC America has invested over $187 million since 2019 and is continuing to invest in infrastructure projects, including the upcoming FANUC Academy, an advanced automation customer training center. The company's expansion has created over 400 jobs in Michigan, and it is fortifying its position in North America with ongoing investments.
Skild AI grabs $300M to build foundation model for robotics
Skild AI, a Pittsburgh-based startup, has secured a $300 million Series A funding round, boosting its valuation to $1.5 billion. Led by top investors like Lightspeed Venture Partners, Coatue, SoftBank Group, and Bezos Expeditions, Skild AI is focused on developing smart robots with embodied intelligence, creating the Skild Brain, a versatile AI model for various robot types and tasks.
Shanghai Publishes First-Ever Humanoid Robot Governance Guidelines
Chinese AI and legal groups have published the first-ever governance guidelines for humanoid robots at the World Artificial Intelligence Conference (WAIC) 2024 in Shanghai. The guidelines aim to ensure responsible development of humanoid robots by emphasizing human safety and dignity. They include measures for risk procedures, emergency response mechanisms, and ethical and lawful use training for companies developing humanoid robots. The initiative also seeks to establish a global framework for governing machines related to humanoid robots.
Robot Research In The News
Researchers have developed a new algorithm to improve the movement of two-legged robots on challenging surfaces like stairs. The algorithm combines ankle movement with a model called the angular momentum-based linear inverted pendulum (ALIP), allowing the robot’s center of mass to change height. It uses a dual-controller system to precisely control the robot's movements and ensure walking stability. The algorithm has been tested on the Cassie robot and has shown success, even allowing the robot to use a moving walkway.
Low-cost actuators offer new twist on artificial 'muscles' for safer, softer robots
Northwestern University engineers have developed a soft, flexible actuator that enables robots to move like human muscles. The actuator, made from common rubber, costs about $3 in materials excluding the motor, making it cost-effective. The research aims to create inexpensive, flexible robots for tasks in human environments. The team used 3D printing to create cylindrical structures called "handed shearing auxetics" (HSAs) out of rubber, allowing the robots to bend and deform easily. These advancements bring us closer to bioinspired robots that move like living organisms, opening up new possibilities for tasks that traditional robots cannot perform.
Robot Workforce Story Of The Week
UK’s Assured Skills Academy in Robotics and Automation Opens To Applicants
Funded by the Department for the Economy, South West College (SWC) is offering a Robotics and Automation training program for 12 individuals, aimed at preparing them for potential roles in Dungannon and surrounding areas. This 14-week part-time course, running from September 2 to December 13, includes training on Monday and Wednesday evenings, and Friday afternoons. Participants will receive a £52.50 weekly training allowance, with support for travel and childcare costs.
Mr. Murphy highlights the academy's role in strengthening the local skills base and providing high-quality training that meets employer needs. Padraig McNamee of SWC emphasizes the program’s focus on Industry 4.0 technologies, offering hands-on experience with cutting-edge industrial technologies. Maria Curran from MEGA underscores the importance of having a workforce trained in the latest advancements to enhance industry competitiveness.
Graduates will earn industry-recognized qualifications and are guaranteed an interview with supporting companies. No prior experience is required, and the program is designed to be flexible to accommodate current commitments.
Interested individuals must apply online by noon on August 2, be at least 18 years old by September 2, and eligible to work in the UK. For more information, visit nidirect.gov.uk or email assuredskills@economy-ni.gov.uk.
Robot Video Of The Week
Using a new type of surgical intervention and neuroprosthetic interface, MIT researchers, in collaboration with colleagues from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, have shown that a natural walking gait is achievable using a prosthetic leg fully driven by the body’s own nervous system. The surgical amputation procedure reconnects muscles in the residual limb, which allows patients to receive “proprioceptive” feedback about where their prosthetic limb is in space. Read more here.
Upcoming Robot Events
July 17-21 RoboCup (Eindhoven)
Aug. 6-9 International Woodworking Fair (Chicago, IL)
Sept. 9-14 IMTS (Chicago, IL)
Oct. 1-3 International Robot Safety Conference (Cincinnati, OH)
Oct. 7 Humanoid Robot Forum (Memphis, TN)
Oct. 8-10 Autonomous Mobile Robots & Logistics Conference (Memphis, TN)
Oct. 14-18 International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (Abu Dhabi)
Oct. 15-17 Fabtech (Orlando, FL)
Oct. 16-17 RoboBusiness (Santa Clara, CA)
Oct. 21-23 ROSCon (Odense, Denmark)
Oct. 28-Nov. 1 ASTM Intl. Conference on Advanced Manufacturing (Atlanta, GA)
Nov. 22-24 Humanoids 2024 (Nancy, France)