You May Lose Your Job To A Robot...In China
China is investing more in Robotics than any other country
Aaron’s Thoughts On The Week
"China has become the world's largest market for industrial robots, driven by an increase in demand for automation in manufacturing, which is a critical strategy for the country's future economic growth and global competitiveness." - Jeff Burnstein, President of the Association for Advancing Automation (A3)
The rapid advancement of robotics in China has been nothing short of remarkable. Once seen as a manufacturing hub relying on cheap labor, China has become a global leader in robotics and automation, overtaking countries like the United States. According to the International Federation of Robotics (IFR), China has become the world’s largest industrial robot market and is also emerging as a powerhouse in robotics innovation and development.
This transformation was on full display at last week’s World Robotics Conference in Beijing, an event that underscored China's growing influence in the global robotics landscape. The conference, one of the most significant gatherings for robotics professionals, researchers, and businesses worldwide, highlighted the country’s progress and ambitions in the field of robotics and AI. Featuring over 600 exhibitors from more than 20 countries, the event showcased cutting-edge technologies, research, and applications that are driving the next wave of robotics innovation.
A Booming Market for Industrial Robots
In the last decade, China's robotics market has grown at an unprecedented rate, establishing the country as a global leader in automation. The International Federation of Robotics (IFR) 2023 World Robotics Report reveals that China installed nearly 290,000 industrial robots in 2022 alone, accounting for 52% of all global installations that year. This remarkable figure dwarfs robot installations in other major markets, such as Japan, South Korea, and the United States. Over the past five years, the growth rate of robot installations in China has averaged around 25% annually, significantly outpacing the global average growth rate of 11%.
Factors Driving China's Robotics Dominance
China's leadership in the robotics sector is primarily driven by a strategic focus on automation to boost productivity and maintain a competitive edge in global manufacturing. As labor costs continue to rise, Chinese companies are increasingly adopting robotics to achieve higher levels of precision, efficiency, and scalability. This trend is particularly evident in industries such as automotive, electronics, and metalworking, which have been at the forefront of integrating robots into their production lines.
Automotive Industry: The automotive sector has long been a significant driver of robotic adoption in China. As the world's largest car market and production base, including a rapidly expanding electric vehicle (EV) sector, the demand for automation in car manufacturing is immense. Automakers are leveraging robots for welding, painting, assembly, and quality control to increase production efficiency and reduce costs.
Electronics and Semiconductor Industry: Since 2016, the electronics and semiconductor industries have overtaken automotive as the largest consumer of industrial robots in China. The country is a global leader in producing electronic devices, batteries, semiconductors, and microchips, which require high-precision manufacturing processes. Robots are essential for tasks such as assembly, testing, and packaging, enabling companies to scale up production while maintaining high quality.
Metalworking and General Manufacturing: The metalworking industry, which includes machine tool manufacturing and metal forming, has also seen substantial growth in robot adoption. Robots help manufacturers improve product quality and worker safety, reduce waste, and enhance overall productivity.
Government Support and Strategic Initiatives
The Chinese government has significantly fostered the growth of its robotics industry through initiatives like "Made in China 2025," which aims to modernize the manufacturing sector by integrating advanced technologies such as robotics and artificial intelligence (AI). This strategy is supported by substantial financial backing to accelerate robotics adoption across various sectors, including subsidies, tax incentives, and R&D funding. The goal is to reduce dependency on foreign technology and advance up the manufacturing value chain.
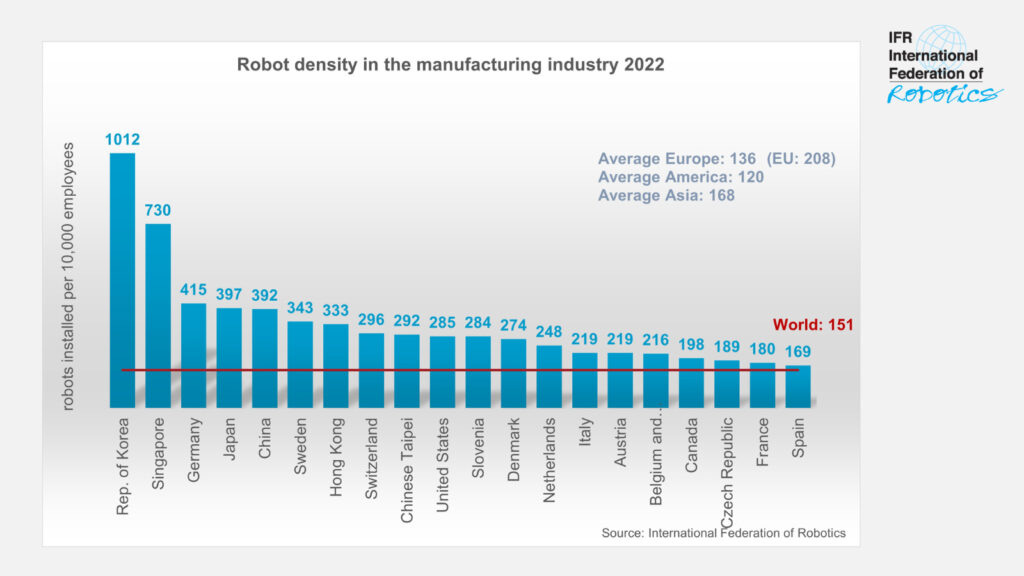
China’s push for automation aligns with its broader economic strategy. The country has achieved a robot density of 322 units per 10,000 employees in manufacturing as of 2022, surpassing the United States' 274 units. At the recent Third Plenum of the 20th National Congress, the Chinese government reiterated its focus on robotics as a key driver for economic growth, emphasizing the country’s unique position as the world’s largest robotics market.
Technological Advancements, Domestic Innovation, and the Rise of Humanoid Robotics in China
China's robotics industry has undergone a remarkable transformation, evolving from heavy reliance on foreign technologies to becoming a significant innovator in its own right. Over the past decade, Chinese robotics companies like Siasun, DJI, Geek+, and emerging humanoid robotics firms such as Unitree Robotics and Fourier Intelligence have become global leaders. They are developing advanced robotic solutions across various sectors, including industrial automation, logistics, healthcare, services, and now humanoid robotics. This shift marks a move from simple mass production to a focus on sophisticated, high-tech robotics that integrate AI, machine learning, advanced sensor technologies, and human-robot interaction.
Emergence of Key Domestic Players
Siasun Robotics: Siasun is one of China's top robotics companies, specializing in a wide range of industrial robots, including collaborative robots (cobots) that can work safely alongside humans in factory settings. The company is pioneering intelligent robotic solutions, aiming to reduce the technological gap with global giants like ABB and KUKA. Siasun invests heavily in R&D to develop robots that are more flexible, safe, and easy to use, catering to a variety of industries beyond traditional manufacturing.
DJI: Known globally for its dominance in the drone market, DJI has leveraged its expertise in AI, computer vision, and robotics to expand into new areas like autonomous systems for logistics and emergency response. DJI’s advanced navigation and AI capabilities are critical in developing robots that can operate autonomously in complex environments, including agriculture and public safety.
Geek+: Geek+ is a leader in logistics automation, specializing in autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) and intelligent warehousing solutions. These robots, powered by advanced AI algorithms, can navigate complex environments, manage inventories, and optimize warehouse operations autonomously. Geek+ has deployed thousands of robots globally, showcasing China's ability to produce high-quality, competitive robotic solutions that are scalable and adaptable.
Unitree Robotics: Known for its development of quadruped robots and, more recently, humanoid robots, Unitree Robotics is at the forefront of China’s push into humanoid robotics. Its robots, like the Unitree Go1, are designed for agility, flexibility, and versatility, suitable for both research and practical applications. The company is investing in creating robots that can perform tasks in unstructured environments, making them suitable for logistics, security, and even household tasks.
Fourier Intelligence: Specializing in rehabilitation robotics, Fourier Intelligence has been developing advanced humanoid robots that blend robotics with AI to assist in healthcare settings. Their humanoid robots are designed to interact seamlessly with humans, providing therapy, support, and companionship, particularly for elderly care. The company is expanding its offerings to include robots that can be integrated into everyday environments, aligning with China’s demographic needs.
Moving Beyond Traditional Robots: Advanced and Humanoid Robotics Systems
Chinese robotics companies are rapidly advancing from traditional industrial robots to more sophisticated and integrated systems, including collaborative robots (cobots), autonomous mobile robots (AMRs), intelligent warehousing solutions, and humanoid robots:
Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Cobots are designed to work with humans safely and efficiently, enhancing productivity without needing extensive safety barriers. Companies like Siasun and Aubo Robotics are developing versatile cobots that can be deployed across various industries for assembly, quality inspection, and material handling tasks. This trend has helped Chinese firms make inroads into markets previously dominated by Western companies.
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs): Companies like Geek+ and ForwardX Robotics are leaders in the development of AMRs, which are increasingly used in logistics and manufacturing for their ability to navigate complex environments autonomously and efficiently manage tasks such as picking, packing, and transportation. Their advanced AI and sensor technologies enable these robots to operate safely and effectively in dynamic settings.
Intelligent Warehousing and Humanoid Robotics: The robotics industry in China is expanding into intelligent warehousing solutions, integrating AI and robotics to optimize supply chain operations. Geek+ and others are deploying fully automated systems that handle inventory management and order fulfillment, solidifying their role as global leaders in logistics automation. Simultaneously, firms like Unitree Robotics and Fourier Intelligence are developing humanoid robots capable of interacting with humans more naturally and intuitively. These robots are being designed for tasks ranging from logistics and healthcare to personal assistance and entertainment, leveraging AI to understand and respond to human behaviors.
Heavy Investment in R&D and Innovation
To close the gap with established global players like ABB, Fanuc, and KUKA, Chinese robotics firms are making significant investments in R&D. This investment focuses on enhancing AI integration, machine learning, sensor technology, and cloud computing to create robots that are smarter, more flexible, and capable of performing complex tasks autonomously. The government's "Made in China 2025" strategy supports these efforts by prioritizing self-reliance in key technologies, including robotics and AI.
These efforts are paying off. Chinese robotics companies are not only capturing substantial market share domestically but are also expanding their reach internationally. By combining technological advancements with cost advantages and strategic partnerships, Chinese robotics firms, including those in humanoid robotics, are becoming formidable players on the global stage.
Outpacing the United States and Other Developed Economies
China’s rise in robotics has put it ahead of traditional automation leaders like the United States. The U.S., while still a significant player, has been outpaced in terms of both robot installations and market growth. The IFR report shows that the U.S. market installed around 39,000 industrial robots in 2022, which, although significant, pales in comparison to China's figures.
Factors Behind the Gap Between China and the U.S.
Several key factors contribute to the widening gap between China and the United States in terms of robotics adoption:
Scale of Manufacturing Base: China's vast manufacturing base is significantly larger than that of the United States, providing a more substantial market for robotic installations. The sheer scale of industries such as electronics, automotive, and heavy machinery in China drives higher demand for automation technologies to improve efficiency and productivity.
Government Incentives and Faster Adoption: Chinese manufacturers are highly incentivized by government policies, subsidies, and strategic initiatives like "Made in China 2025" to adopt new automation technologies quickly. In contrast, the U.S. faces challenges such as higher costs, regulatory hurdles, and a relatively slower adoption rate among small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), which often need more financial resources or expertise to invest in advanced robotics.
Cost Factors and Regulatory Environment: Robotics implementation costs are often higher in the U.S. due to labor costs, installation expenses, and the need for compliance with stringent safety and regulatory standards. These factors can slow down the pace of adoption compared to China, where lower labor costs and a more flexible regulatory environment support faster deployment of automation technologies.
Robotics Landscape in Other Countries: Japan, South Korea, and Germany
While China's growth in robotics is unprecedented, other countries like Japan, South Korea, and Germany continue to be strong players in the global robotics landscape. These countries have unique strengths and are contributing to the overall growth of the robotics industry in different ways:
Japan: Japan has been a pioneer in robotics for decades and remains one of the leading countries in robot density, with around 399 robots per 10,000 employees in the manufacturing sector. Japanese companies like Fanuc, Kawasaki, and Yaskawa are world leaders in industrial robotics, especially in sectors such as automotive and electronics manufacturing. Japan focuses heavily on robotics innovation, particularly in service and healthcare robots, as its aging population drives demand for robots that can assist with elder care and domestic tasks.
South Korea: South Korea boasts the highest robot density in the world, with over 1,000 robots per 10,000 workers in the manufacturing sector, driven primarily by the automotive and electronics industries. Companies like Hyundai Robotics and Samsung Robotics are leading the development of both industrial and service robots. South Korea's government has also introduced policies to support the growth of robotics, such as tax incentives and funding for R&D. The country is focusing on next-generation robotics technologies, including AI integration and autonomous systems, to maintain its leadership in this sector.
Germany: As the leader in robotics within Europe, Germany is renowned for its high-quality engineering and innovation in robotics and automation. Germany’s robot density is among the highest in the world, with about 371 robots per 10,000 employees. German companies like KUKA (which is owned by a Chinese company), ABB (with a strong presence in Germany), and Siemens are at the forefront of developing advanced industrial robots, particularly for precision manufacturing in automotive and electronics. The country’s focus on Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing has positioned it as a global leader in integrating robotics with digital technologies, such as IoT and AI.
Challenges and Opportunities for Other Countries
While countries like Japan, South Korea, and Germany maintain strong positions in robotics, they face challenges similar to the United States, including high costs, aging workforces, and regulatory complexities. However, these countries are leveraging their strengths in innovation, high-quality manufacturing, and government support to continue advancing their robotics industries.
Japan is focusing on developing more autonomous and AI-driven robots for diverse applications beyond manufacturing, such as healthcare and service sectors, to adapt to demographic changes and maintain growth.
South Korea is leveraging its leadership in electronics and automotive manufacturing to develop cutting-edge robotics technologies, with a significant emphasis on export markets to sustain growth.
Germany is integrating robotics with advanced digital technologies, focusing on creating more flexible, networked, and intelligent manufacturing systems to align with Industry 4.0 trends.
Future Prospects and Challenges
Looking ahead, China’s leadership in robotics is poised to solidify further as it plans for the next wave of automation, integrating AI with robotics to create more intelligent, adaptive, and autonomous systems. The Chinese government continues to make significant investments in building a robust robotics ecosystem, spanning research and development (R&D), talent cultivation, manufacturing, and global exports. This is all part of China's strategic goal to become a global leader in advanced robotics and AI, as highlighted in its "Made in China 2025" initiative and its more recent "14th Five-Year Plan" for robotics development.
China's Strategic Focus on AI and Robotics Integration
China's commitment to advancing AI-driven robotics is evident in its strategic plans and investments. The country is focusing on enhancing the capabilities of robots by integrating AI, machine learning, and big data to create systems that are not only more autonomous but also more adaptable to various environments and applications. This includes the development of next-generation robotics for industries such as healthcare, logistics, automotive, and manufacturing. According to a report by the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology (CAICT), the Chinese government has committed to investing billions in AI and robotics R&D, with a focus on creating intelligent robots that can function autonomously in dynamic environments.
Government Initiatives to Boost the Robotics Ecosystem
China's government initiatives are central to its success in the robotics sector. The "14th Five-Year Plan for Robotics Industry Development," released in 2021, emphasizes enhancing core technological capabilities, expanding the applications of robotics in various sectors, and promoting international cooperation. It sets specific goals for developing high-end robotics components, such as controllers, sensors, and servo motors, to reduce dependency on imports and ensure self-reliance in critical technologies. Additionally, policies are in place to foster talent development by supporting robotics education and establishing innovation hubs and research centers across the country.
Challenges and Market Fragmentation
Despite these ambitious plans, several challenges could hinder China's trajectory toward robotics supremacy. One significant issue is the fragmentation of the robotics market. With numerous domestic players competing fiercely, the market has become highly fragmented, leading to inconsistencies in quality and standards. While this competition can drive innovation, it also creates challenges in terms of scalability and the ability to maintain uniform quality across products.
Intellectual Property and Quality Control Concerns
Intellectual property (IP) concerns are another major issue. While China has made strides in improving its IP protection laws, foreign companies and investors often remain wary due to the risk of technology theft or IP infringement. This has been a significant barrier to deeper collaboration between Chinese firms and global technology leaders. Quality control also remains a challenge, especially for high-precision robotics needed in industries like healthcare and aerospace. As China moves toward more complex and high-stakes applications, maintaining rigorous quality standards will be critical.
Shortage of Skilled Professionals
Another pressing issue is the shortage of skilled professionals needed to manage and advance complex robotic systems. As the industry evolves, there is a growing demand for highly skilled engineers, data scientists, and AI specialists. The Chinese government has recognized this gap and is investing in education and training programs, but the demand still far outstrips supply. This shortage could limit the pace at which China can innovate and maintain its competitive edge in the global robotics arena.
What This All Means
The rapid rise of China in the field of robotics presents a growing concern for other global powers like the United States, Japan, Germany, and South Korea. China has emerged as the world’s largest industrial robot market, with its strategic focus on automation and technological innovation driving unprecedented growth. At the 2024 World Robotics Conference in Beijing, China showcased its dominance, revealing a staggering installation of nearly 290,000 industrial robots in 2022 alone, far outpacing other nations. With its "Made in China 2025" initiative, China is not just manufacturing more robots; it is investing heavily in advanced AI, robotics, and humanoid technologies to leap ahead in global innovation.
Those who want to, at a minimum, keep up with China are going to need a plan similar to “Made in China 2025” for their own countries. As shown, some countries like South Korea do have a national plan. However, too many, including the US, appear to just let the market decide the proper amount of robotics and supporting industries there will be for both the short term and long term. While this may hold to some of the guiding principles of their economy, when looking at it through a global scale, it is setting up for failure in the long term.
While there's no guarantee that China will become the world's leading robotics giant, it's impossible to overlook their rapid growth and substantial investment in robotics development within the country. Numerous factors could potentially hinder China's ambitions, but having a transparent plan and successfully executing it helps mitigate the risks of failure. Ultimately, it's this strategic planning that will determine China's future position in the robotics industry. While China has a clear roadmap, other countries must develop their own plans or risk being surpassed by China, which is aggressively driving progress forward.
TL;DR
China has rapidly become a global leader in robotics and automation, with the country installing nearly 290,000 industrial robots in 2022, accounting for 52% of global installations. This growth has been driven by strategic government support and substantial investments in AI, robotics, and manufacturing technologies. China’s focus on automation is evident in industries like automotive, electronics, and metalworking. The country’s robot density reached 322 units per 10,000 employees in 2022, surpassing the U.S. and other developed economies. As China continues to invest heavily in robotics R&D, it is poised to solidify its position as a global leader in robotics and automation.
Robot News Of The Week
Skyline Robotics deploys Ozmo window cleaning robot in New York City
Skyline Robotics collaborates with Palladium Window Solutions and The Durst Organization to deploy its Ozmo robot, equipped with a KUKA robotic arm, to clean windows on a 45-story skyscraper in New York City. The system uses machine learning, computer vision, and advanced sensors to autonomously clean windows three times faster than traditional methods while maintaining high safety standards. Skyline Robotics aims to revolutionize the window-cleaning industry, addressing labor shortages and enhancing safety. The company plans to expand globally and introduce its robotics-as-a-service (RaaS) model in markets like London, Japan, Singapore, and South Korea.
Robots Are Starting (Good) Fires in California
Cody Chiverton, a former firefighter, has joined BurnBot, a startup in San Francisco that uses robotic technology for wildfire management. The company's robot, the BurnBot RX1, can clear vegetation without producing flames or smoke. BurnBot aims to make prescribed burns more efficient, requiring fewer personnel and minimizing environmental risks. With $25 million raised so far, the company plans to expand its services to more U.S. states, Canada, and Australia. However, challenges remain, such as refining the technology to withstand extreme conditions and convincing traditional fire authorities to adopt new methods.
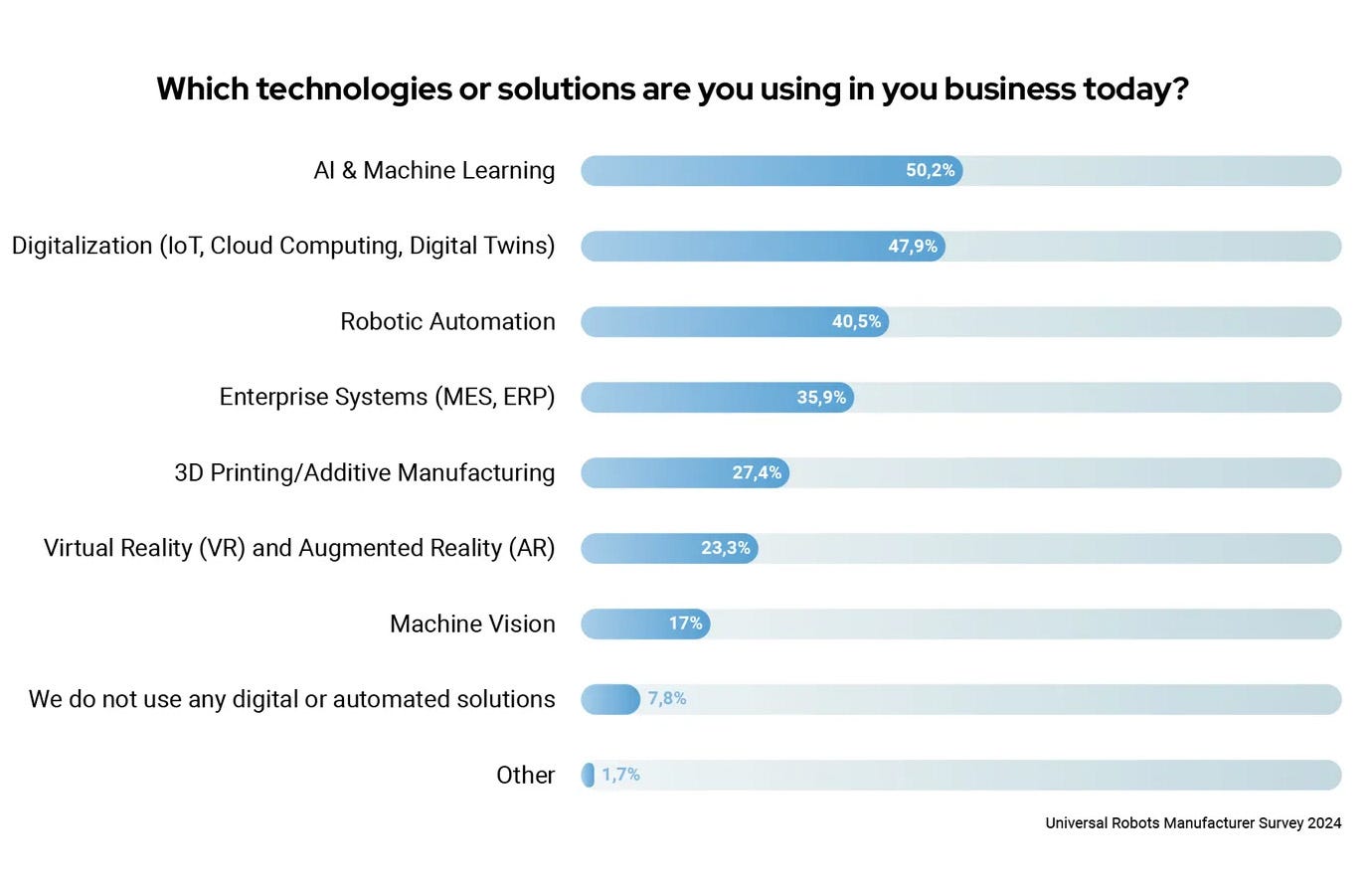
UR survey shows 48% of manufacturers plan to invest in AI
The AI market is projected to reach $407 billion by 2027, with over 50% of manufacturers already using AI and ML in their production processes. 48% plan to invest further in AI and ML by 2025, and about 47% use digital tools for optimization. The top reasons for adopting AI and robotics include improving product quality, increasing productivity, and enhancing accuracy. Primary concerns include return on investment and usability.
Robot Research In The News
Researchers develop a new humanoid platform for robotics research
Researchers at UC Berkeley developed the Berkeley Humanoid, a new low-cost, robust robotic platform designed for academic research in humanoid robotics. Unlike existing platforms, it is affordable, easy to maintain, and adaptable for various locomotion tasks. Built with custom mechanical and electrical components, the Berkeley Humanoid is highly reliable and supports learning-based control. Future developments include adding arms and perception capabilities to enhance its research applications in robot control and navigation.
These Robots Get a Power-Up From Mushrooms
Researchers at Cornell University are exploring the potential of fungi to control future robots, aiming to create more versatile and durable biohybrid machines. Traditional fully mechanical robots need to catch up to animals in efficiency and adaptability. While previous biohybrid experiments have used animal tissues or plant cells, fungi offer unique advantages due to their resilience and easy cultivation.
The Cornell team, led by Associate Professor Robert Shepherd, experimented by culturing mycelia, the root-like structures of king oyster mushrooms, in a 3D-printed scaffold with built-in electrodes. As the mycelia grew and fused onto the electrodes, they could generate electrical signals when exposed to ultraviolet light. These signals were successfully used to control a starfish-shaped robot's movements, as well as a four-wheeled robot.
The fungi demonstrated potential for long-term responsiveness to environmental changes, suggesting applications in fields like agriculture or security. However, challenges remain, such as signal degradation over time and the fungi's tendency to die, requiring further research to enhance signal amplification and regeneration.
While the concept of fungi-driven robots may sound like science fiction, this research indicates that fungi could play a significant role in the future of robotics—albeit with some hurdles to overcome before practical deployment.
Robot Workforce Story Of The Week
NorthWest Arkansas Community College adding new high school robotics program
NorthWest Arkansas Community College is offering a new robotics program for high school students. The program provides robotics and electronics certifications through concurrent courses at the college, helping students find jobs in areas like robot operation and programming, production engineering, and technology maintenance after graduation.
Robot Video Of The Week
Boston Dynamics has revealed the new capabilities of its electric Atlas humanoid robot in a recent video, showcasing it performing eight pushups and demonstrating enhanced athletic intelligence and movement. The electric version boasts advanced actuators with increased strength and a broader range of motion compared to its hydraulic predecessor. The company plans to start testing the new Atlas with Hyundai and select partners in 2025, positioning it to compete in the evolving market for humanoid robots alongside other commercial humanoids from competitors like Agility Robotics and Figure AI.
Upcoming Robot Events
Sept. 9-14 IMTS (Chicago, IL)
Oct. 1-3 International Robot Safety Conference (Cincinnati, OH)
Oct. 7 Humanoid Robot Forum (Memphis, TN)
Oct. 8-10 Autonomous Mobile Robots & Logistics Conference (Memphis, TN)
Oct. 14-18 International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (Abu Dhabi)
Oct. 15-17 Fabtech (Orlando, FL)
Oct. 16-17 RoboBusiness (Santa Clara, CA)
Oct. 21-23 ROSCon (Odense, Denmark)
Oct. 28-Nov. 1 ASTM Intl. Conference on Advanced Manufacturing (Atlanta, GA)
Nov. 22-24 Humanoids 2024 (Nancy, France)
Jan. 21-24 Intl. Symposium on System Integrations (Munich)
Mar. 4-6 Intl. Conference on Human-Robot Interaction (Melbourne)
Mar. 21-23 Intl. Conference on Robotics and Intelligent Technology (Macau)
May 12-15 Automate (Detroit, MI)
May 17-23 ICRA 2025 (Atlanta, GA)
May 18-21 Intl. Electric Machines and Drives Conference (Houston, TX)
May 20-21 Robotics & Automation Conference (Tel Aviv)
Aug. 18-22 Intl. Conference on Automation Science & Engineering (Anaheim, CA)